GeoModeling
TexNet Geomodeling
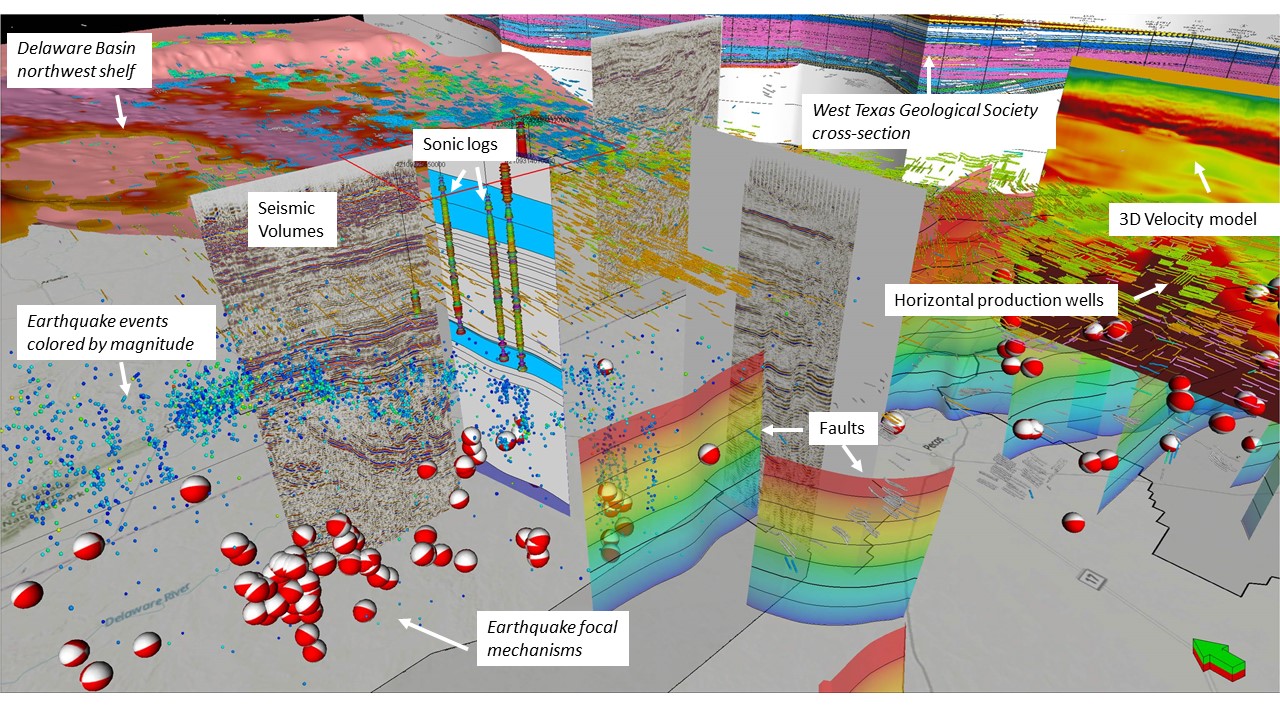
Geomodeling uses all available geophysical and geological data to create a three-dimensional (3D) representation of the subsurface. Geomodeling is the number one tool for planning and decision-making for a wide range of applications, such as well stimulation projects, carbon capture and storage, seismicity analysis, etc. The TexNet geomodeling group focuses on building integrated, multidisciplinary 3D geomodels. The group builds each model by first integrating outcrop, core, and well-log correlations, 3D seismic, and seismicity data into high-resolution 3D models. The group then performs structural and seismic stratigraphic interpretation utilizing next-generation 3D interpretation tools starting in the time domain with a focus on creating the most accurate 3D subsurface framework needed to constrain the lateral and vertical velocity distributions. Advanced techniques such as geomorphology-based modeling (stratal slicing) are critical to properly capturing precise chrono- and lithostratigraphy. The group then uses sophisticated fault interpretation and automated fault extraction techniques to build faulted frameworks. Following time-depth conversion, the TexNet geomodeling group combines facies interpretations obtained from core and seismic attribute analysis with insights into the depositional environment to build an accurate 3D facies architecture. Next, the group uses petrophysical parameters derived from well logs and core to obtain 3D facies-conditioned distributions of rock and fluid parameters. From this data, the group constructs a high-resolution 3D velocity model to aid in accurately locating or relocating seismic events. They integrate all historical water injection into the model. Finally, the TexNet geomodeling group uses these models to analyze the geological, engineering, petrophysical, geophysical, and geomechanical drivers of local seismicity.